Creación y personalización de una gráfica en Matplotlib — 12:05 min
12:05 min | Última modificación: Octubre 6, 2021
Matplotlib es una de las principales librerías utilizadas para graficación de datos en Python. En este tutorial se explica como crear y personalizar un gráfico simple.
Matplotlib cheatsheets: https://github.com/matplotlib/cheatsheets#cheatsheets
Datos
[1]:
#
# Se desean graficar las ventas mensuales en $.
# Las cantidades están en K
#
data = {
"month": [
"jan",
"feb",
"mar",
"apr",
"may",
"jun",
"jul",
"aug",
"sep",
"oct",
"nov",
"dic",
],
"amount": [333, 335, 445, 475, 560, 720, 950, 1090, 1380, 1162, 934, 860],
}
Gráfico inicial
[2]:
#
# Se verifica que se tenga una gráfica con
# valores de sus parámetros por defecto.
#
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.bar(
x="month",
height="amount",
width=0.8,
bottom=None,
data=data,
)
plt.show()
Paso 1: Tamaño del gráfico
[3]:
#
# Paso 1: se ajusta el tamaño del grafico.
#
plt.figure(figsize=(9, 6))
plt.bar(
x="month",
height="amount",
width=0.8,
bottom=None,
data=data,
)
plt.show()
Paso 2: Se agrega el títulos y los nombres de los ejes.
[4]:
plt.figure(figsize=(9, 6))
plt.bar(
x="month",
height="amount",
width=0.8,
bottom=None,
data=data,
)
plt.title("Sold Units", fontsize=18)
plt.xlabel("Month", fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel("Amount")
plt.show()
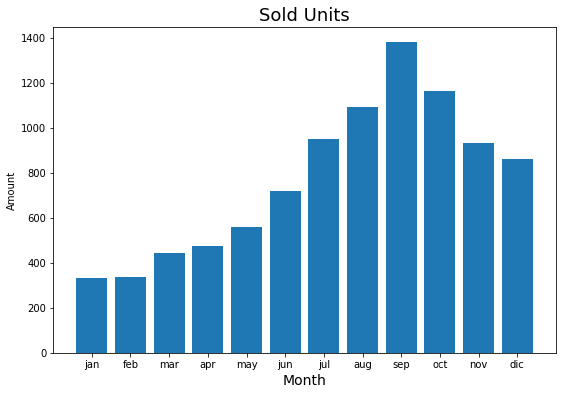
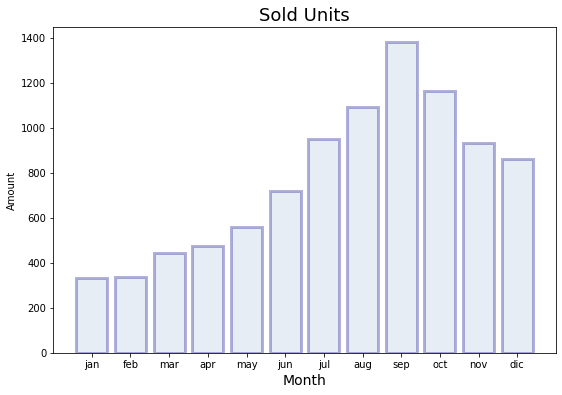
Paso 3: Se personalizan las barras
[5]:
plt.figure(figsize=(9, 6))
plt.bar(
x="month",
height="amount",
width=0.8,
bottom=None,
data=data,
#
color="lightsteelblue",
alpha=0.3,
edgecolor="darkblue",
linewidth=3,
)
plt.title("Sold Units", fontsize=18)
plt.xlabel("Month", fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel("Amount")
plt.show()
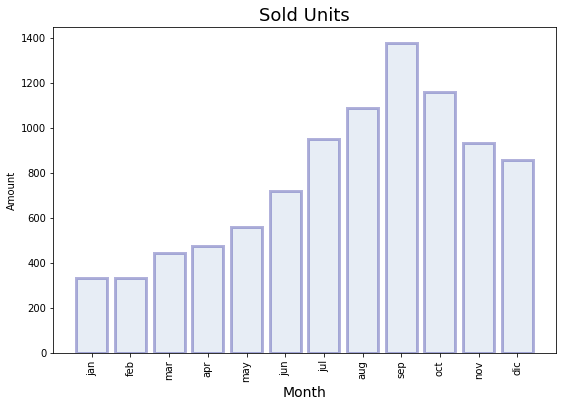
Paso 4: Se formatea el eje X
[7]:
plt.figure(figsize=(9, 6))
plt.bar(
x="month",
height="amount",
width=0.8,
bottom=None,
data=data,
#
color="lightsteelblue",
alpha=0.3,
edgecolor="darkblue",
linewidth=3,
)
plt.title("Sold Units", fontsize=18)
plt.xlabel("Month", fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel("Amount")
plt.xticks(rotation="vertical")
plt.show()
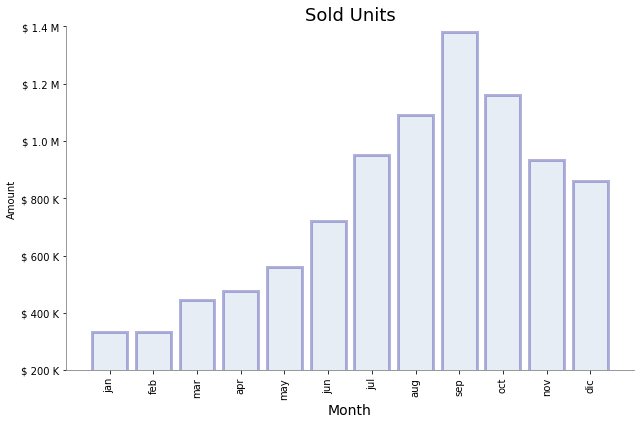
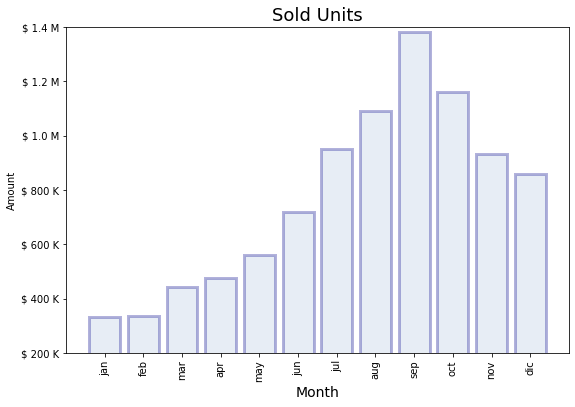
Paso 5: Se formatea el eje Y
[8]:
import matplotlib.ticker as tick
plt.figure(figsize=(9, 6))
plt.bar(
x="month",
height="amount",
width=0.8,
bottom=None,
data=data,
#
color="lightsteelblue",
alpha=0.3,
edgecolor="darkblue",
linewidth=3,
)
plt.title("Sold Units", fontsize=18)
plt.xlabel("Month", fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel("Amount")
plt.xticks(rotation="vertical")
#
# Función para formatear la cantidad. Note
# que retorna un string
#
def yaxis_format(y_value, y_position):
if y_value >= 1e3:
y_formated = "$ {:1.1f} M".format(y_value * 1e-3)
else:
y_formated = "$ {:3.0f} K".format(y_value)
return y_formated
plt.gca().yaxis.set_major_formatter(
tick.FuncFormatter(yaxis_format),
)
#
# Límites del eje Y
#
plt.gca().set_ylim(200, 1400)
plt.show()
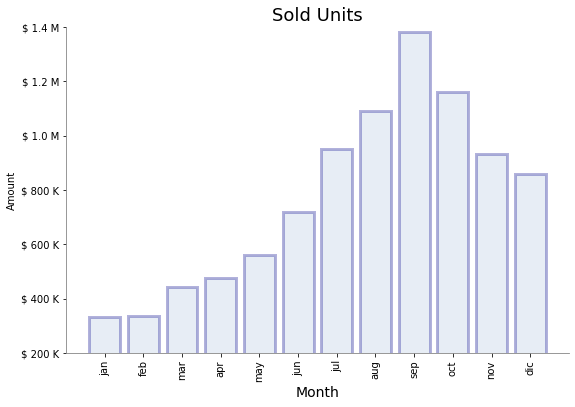
Paso 6: Se formatea el fondo
[9]:
plt.figure(figsize=(9, 6))
plt.bar(
x="month",
height="amount",
width=0.8,
bottom=None,
data=data,
#
color="lightsteelblue",
alpha=0.3,
edgecolor="darkblue",
linewidth=3,
)
plt.title("Sold Units", fontsize=18)
plt.xlabel("Month", fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel("Amount")
plt.xticks(rotation="vertical")
def yaxis_format(y_value, y_position):
if y_value >= 1e3:
y_formated = "$ {:1.1f} M".format(y_value * 1e-3)
else:
y_formated = "$ {:3.0f} K".format(y_value)
return y_formated
plt.gca().yaxis.set_major_formatter(
tick.FuncFormatter(yaxis_format),
)
plt.gca().set_ylim(200, 1400)
plt.gca().spines["left"].set_color("gray")
plt.gca().spines["bottom"].set_color("gray")
plt.gca().spines["top"].set_visible(False)
plt.gca().spines["right"].set_visible(False)
plt.show()
Paso 7: Se ajusta el tamaño de la figura
[10]:
plt.figure(figsize=(9, 6))
plt.bar(
x="month",
height="amount",
width=0.8,
bottom=None,
data=data,
#
color="lightsteelblue",
alpha=0.3,
edgecolor="darkblue",
linewidth=3,
)
plt.title("Sold Units", fontsize=18)
plt.xlabel("Month", fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel("Amount")
plt.xticks(rotation="vertical")
def yaxis_format(y_value, y_position):
if y_value >= 1e3:
y_formated = "$ {:1.1f} M".format(y_value * 1e-3)
else:
y_formated = "$ {:3.0f} K".format(y_value)
return y_formated
plt.gca().yaxis.set_major_formatter(
tick.FuncFormatter(yaxis_format),
)
plt.gca().set_ylim(200, 1400)
plt.gca().spines["left"].set_color("gray")
plt.gca().spines["bottom"].set_color("gray")
plt.gca().spines["top"].set_visible(False)
plt.gca().spines["right"].set_visible(False)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()